
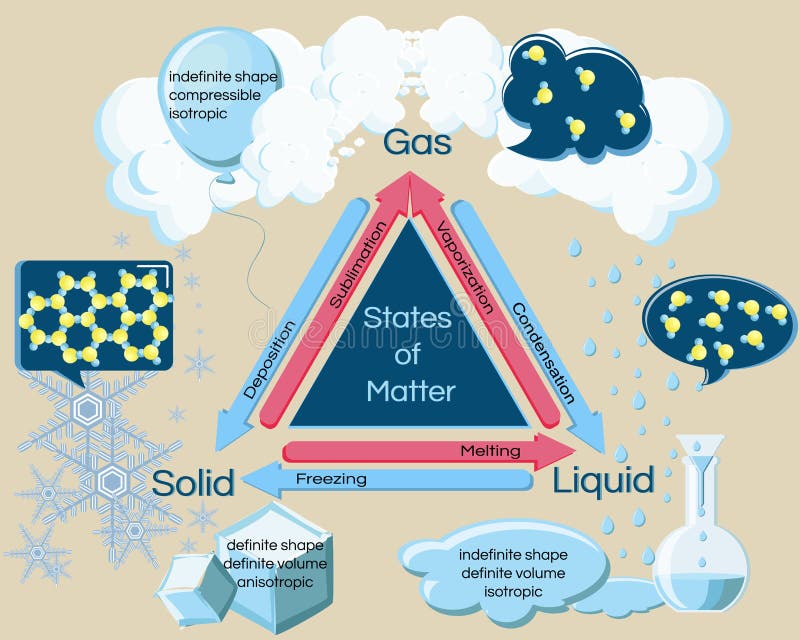
A manometer is a device used to measure pressure in a fluid, particularly a double-legged liquid column gauge used to compare the pressures of two fluids.Vaporization is the process through which a liquid phase changes to a gas phase.A liquid’s boiling point is the temperature at which its vapour pressure falls equivalent to the pressure exerted on the liquid by its surroundings (air). When a liquid is heated to its boiling point, it undergoes rapid vaporization, which is known as boiling.Boiling is a phase change from liquid to gas that happens at or above the boiling point.To evaporate, liquid molecules have to be near the surface, moving in the right direction and have enough kinetic energy to overcome liquid-phase intermolecular interactions.Evaporation is a phase change from the liquid to the gas phase that happens at temperatures lower than the boiling point at a given pressure.Things to Remember based on Phase Changes The six most common phase transitions are melting, freezing, vapor, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. When a substance changes from one state of matter to another, it undergoes a reversible physical change known.During a phase change, energy is either absorbed or released. The type of phase change determines the transfer direction. Energy is exchanged between a material and its environment during a phase change.An iceberg floating in the water, for example, has both a solid and a liquid phase. When two states of the same material exist at the same time, each state is referred to as a phase.During a phase shift, a substance's temperature does not change. A phase change can be identified by monitoring the temperature of a material when it is heated or cooled.Latent heat is defined as the energy required by a substance to either freeze, melt, or boil. Similarly, as a material changes from a gas phase to a liquid phase, its density levels must shift from lower to higher, requiring the substance to release or lose energy to bring the molecules closer together. If a solid changes to a liquid, it must absorb energy to push the molecules into a larger, more fluid volume. In terms of mechanism, latent heat is the effort required to overcome the attractive forces that hold molecules and atoms together in a substance. Latent heat is associated with a heat property called enthalpy.Īn important point to consider regarding latent heat is that the substance’s temperature remains constant. It could be from a gas to a liquid or liquid to solid and vice versa. Latent heat is the heat or energy absorbed or released during the phase change process. It's difficult to find an example of this since it requires a sub-zero temperature. When the reaction takes place, it changes into a soil state without being changed into a liquid, which is the intermediate state. In this case, the substance is in a gaseous state. Depositionĭeposition is the opposite of sublimation. For example, the naphthalene balls used in the households are an example of sublimation. Sublimation is the process by which matter goes from solid to gas without first being transformed into liquid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
